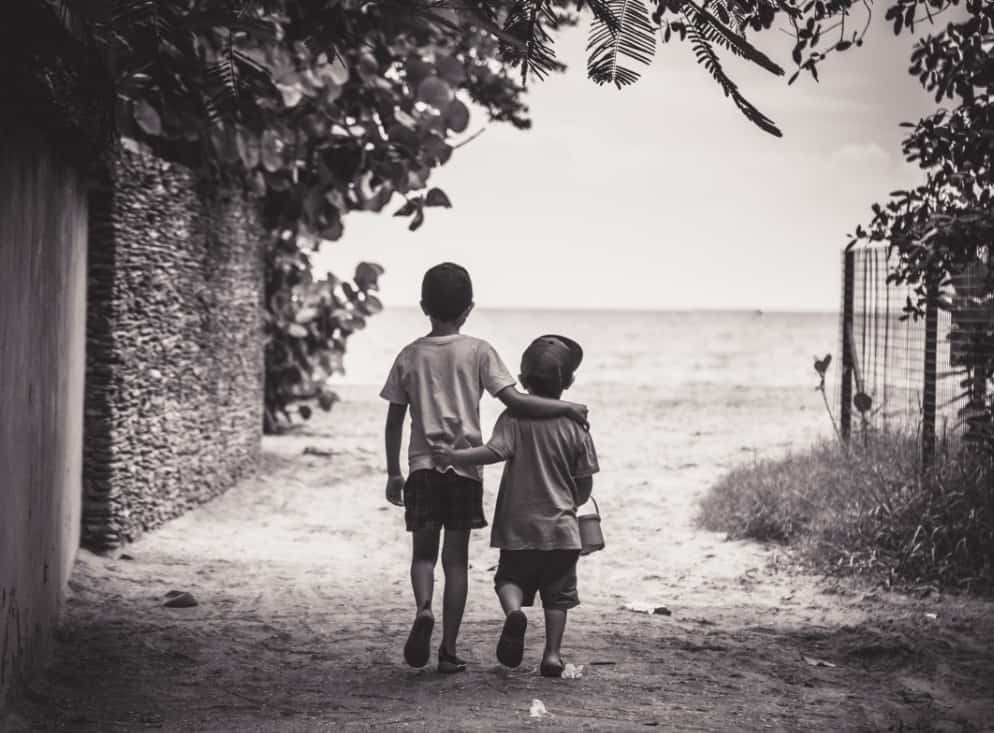
In several Seattle schools, the phrase, “a little child shall lead them” has taken on new meaning. Every few weeks, facilitators of a compassion training program called Roots of Empathy allow a guest “teacher” – a baby from the community – to spark class discussions. Students observe the infant over the course of the year. They ask his parents questions about his behavior and learn about his likes and dislikes. They even help feed and hold him.
Roots of Empathy (ROE) advocates believe that kids can discover the emerging individuality of another human being by bonding with a vulnerable infant. If children develop compassion and protective instincts for a helpless baby, ROE supporters say, then perhaps those emotions will carry over into the way they view their classmates, community members and all citizens of the world.
We all hope our children will grow up to be kind, gracious individuals who leave a positive legacy. But can we be proactive in raising empathetic children? Read on for answers to some key questions parents and educators ask.
Q. What is empathy?
A. Researchers Lynda Haynes and Arthur Avery describe empathy as “…the ability to recognize and understand another person’s perceptions and feelings, and to accurately convey that understanding through an accepting response. 1
Q. Can kids learn empathy?
A. The capacity for empathy exists in all of us. Infants cry or make happy sounds in response to another baby’s noises. Kids as young as two or three often attempt to comfort another child or a parent. 2
Research also links empathy education to a decrease in aggression and at-risk behaviors. Kids who have received empathy training tend to show higher levels of creativity, reading comprehension and critical thinking skills. They problem-solve on a deeper level and are less prone to make shallow or snap judgments. In general, they do better in school. 3
Successful empathy training – whether in the home, in school, or elsewhere – must include helping kids understand others’ feelings and equipping them to act when they see a need they can meet.
Q. What are some practical ways to teach empathy?
A. There are several ways:
- Use books (and other media) to spark discussions about characters’ behaviors, choices and motivations. Ask open-ended questions, like “Why do you think he behaved that way?” or “How did the choice she made impact other people?”
- Help kids verbalize their own feelings so they can learn to recognize others’ emotions.
- Urge children to focus on similarities with others before pointing out differences.
- Role-play. Encourage children to put themselves in someone else’s shoes.
- Familiarize kids with the unknown to diffuse fear and rejection of others. Have a handicapped person demonstrate his artificial limb. Ask a person from another culture to explain his heritage, native traditions or clothing.
- Attribute positive traits to children. “I’ll bet you helped Suzie because you’re such a kind person who likes to help others.”
- Empower children by helping them realize they can bring joy or aid to someone else.
- Praise good behavior and show your disappointment over bad choices — but focus on the act rather than the child.
- Include positive role models in kids’ lives whenever possible. Teach them about godly missionaries, humanitarians and famous philanthropists.
- Cultivate responsibility by expecting children to help around the house and show good manners.
Q. How can parents demonstrate empathy?
A. Research suggests there is no single greater way to teach empathy than by example. Parents can
- Show compassion to others. Take someone a meal or speak kindly to the grocery store clerk.
- Assume the best about other people or their intentions.
- Resolve conflict respectfully, whether it’s with a spouse, a child or a friend.
- Demonstrate responsibly in areas like showing moderation and honoring your commitments.
- Practice patience in your everyday activities, such as driving, standing in line, or dealing with kids.
- Apologize to your children when you’ve done something wrong. They’ll learn its OK to say “I’m sorry.”
- Speak and act with gentleness.
Q. What are some barriers to developing empathy?
A. A number of factors can prevent children from forming healthy levels of empathy. One of the most common examples of this is found in children with reactive attachment disorder (RAD). When a young child’s basic needs for affection and attention go unmet, he will likely struggle all his life to trust and empathize with others.
Other hindrances to empathetic development include:
- Authoritarian or unresponsive parenting
- Parenting guided by threats and guilt trips
- Abuse in the home
- Parents who show prejudice or put others down
- Bribery-centered parenting (since kids may learn to behave well only when a personal reward is involved).
Q. Who provides a good example of empathy?
A. Stories of compassionate individuals – from Mother Teresa and Ghandi to Clara Barton and Albert Schweitzer – pepper the pages of history. While we can learn from their examples, God alone is the root of all empathy. The Bible tells us he is the “source of all comfort” and the One who gives us the ability to comfort others (II Corinthians 1:3-4 NLT).
Christ — the perfect example of compassion —
- drew from His relationship with the Source of empathy.
- was always motivated by love for humanity.
- didn’t judge, condemn, or consider whether people were “worthy” to receive His aid.
- met physical and emotional needs as well as spiritual ones.
- never worried how He would look by helping, but focused on the person in need.
- took the time to understand others’ beliefs, backgrounds, hopes and fears.
Plug your kids in to the Source of all comfort, the Root of all empathy, and you’ll build a firm foundation for raising compassionate kids.